Trading charts are one of the most widely used tools for visualising market movements. In the forex market, they provide a clear view of how currency pairs have moved over time, helping traders observe price trends and market behaviour. By converting raw price data into a visual format, trading charts make it easier to identify patterns and track changes across different timeframes.
Whether it’s a simple line chart showing closing prices or a detailed candlestick chart revealing market sentiment, each type offers unique insights. For forex traders, learning how to read these charts is an essential step in understanding market movements and making informed decisions based on historical and real-time data.
Key Points Summary
- Forex trading charts visually represent currency price movements, helping traders identify trends, patterns, and key market levels.
- Common chart types include line, bar, and candlestick charts, each offering a different level of detail for market analysis.
- Combining chart patterns with tools like moving averages, support and resistance lines, and RSI can provide deeper market insights.
What Is a Forex Trading Chart?
A forex trading chart is a visual representation of how a currency pair’s price has moved over a selected period. It plots price data on a graph, with the vertical axis showing the exchange rate and the horizontal axis representing time. This allows traders to quickly see historical trends, short-term fluctuations, and significant price levels.
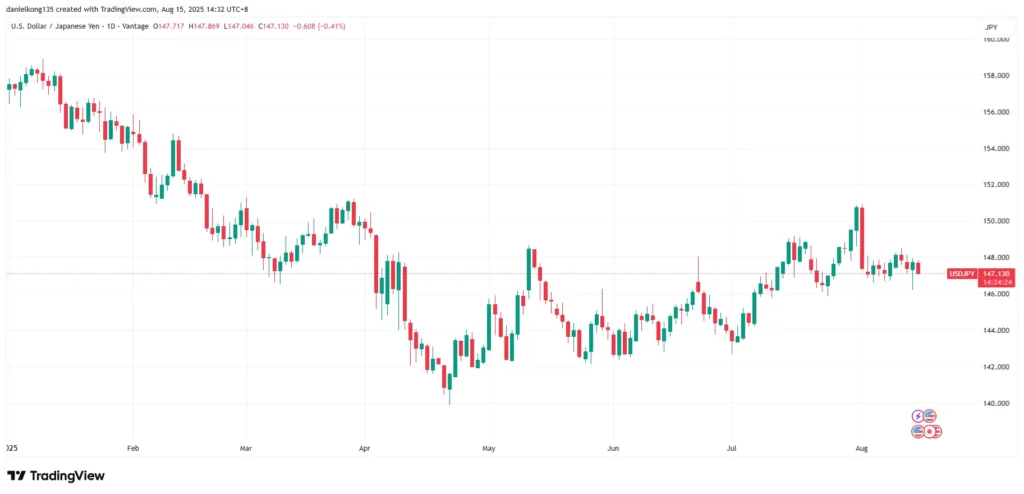
Chart 1: Example of a the USD/JPY daily price chart for 2025. Source: https://www.tradingview.com/x/1KrpLjxy/
These charts form the foundation of technical analysis in the foreign exchange market. By studying the price movements shown in a forex chart, traders can identify patterns, assess market sentiment, and compare historical behaviour with current activity. Common terms for these visual tools include foreign exchange chart, currency trading chart, and forex graph.
While the concept is simple, the detail in a forex trading chart can vary depending on the format used. Some focus on broad trends, while others offer granular insight into price action, trading volume, and specific market events.
Types of Forex Charts and How to Read Them
Forex charts can be presented in several formats, each offering a different level of detail and perspective. Understanding how to interpret these chart types helps traders choose the one that best fits their analysis style and timeframe.
Line Chart in Forex Trading (Line Chart Forex Example)
A line chart is the simplest type of forex chart, plotting a series of closing prices over a set period and connecting them with a continuous line. This clean visual style makes it easy to identify overall trends without the distraction of intraday price fluctuations.
For example, a line chart forex display for EUR/USD might show a smooth upward slope if the pair has consistently closed higher over recent sessions. While line charts are less detailed than other formats, they are effective for tracking long-term direction and comparing multiple currency pairs.
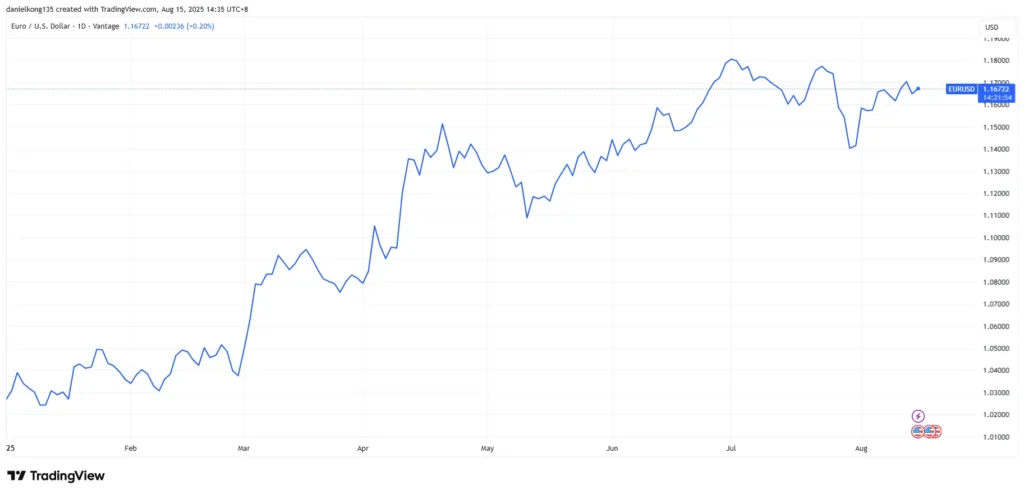
Chart 2: EUR/USD daily price chart for 2025. Source: https://www.tradingview.com/x/NYzPNdBs/
Bar Chart in Forex (OHLC Forex Graph)
A bar chart, also known as an OHLC (Open, High, Low, Close) chart, provides more detail than a line chart. Each vertical bar shows the highest and lowest prices reached during a specific period, while small horizontal ticks on either side indicate the opening and closing prices.
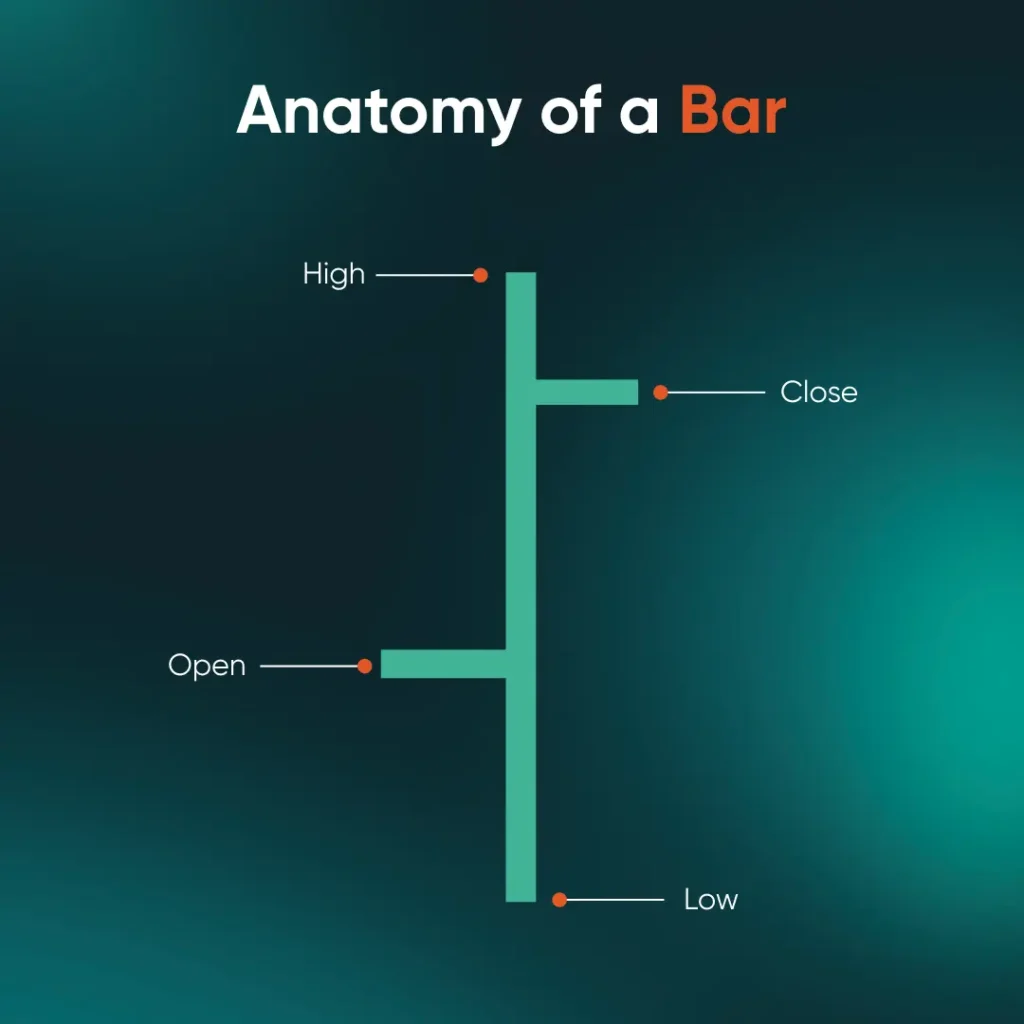
Image 1: Anatomy of a bar
A forex graph in this format can help traders see both the range of price movement and the market’s closing position within that range. This is valuable for spotting volatility and gauging whether buyers or sellers had more control in a given period.
Chart 3: GBP/USD bar chart example.
Candlestick Chart and Patterns in Forex
Candlestick charts are among the most widely used in forex trading. Each candlestick represents price movement over a set time period, displaying the open, high, low, and close in a format that visually reflects market sentiment. A filled or coloured body often signals a price decline, while a hollow or lighter body indicates a price increase.
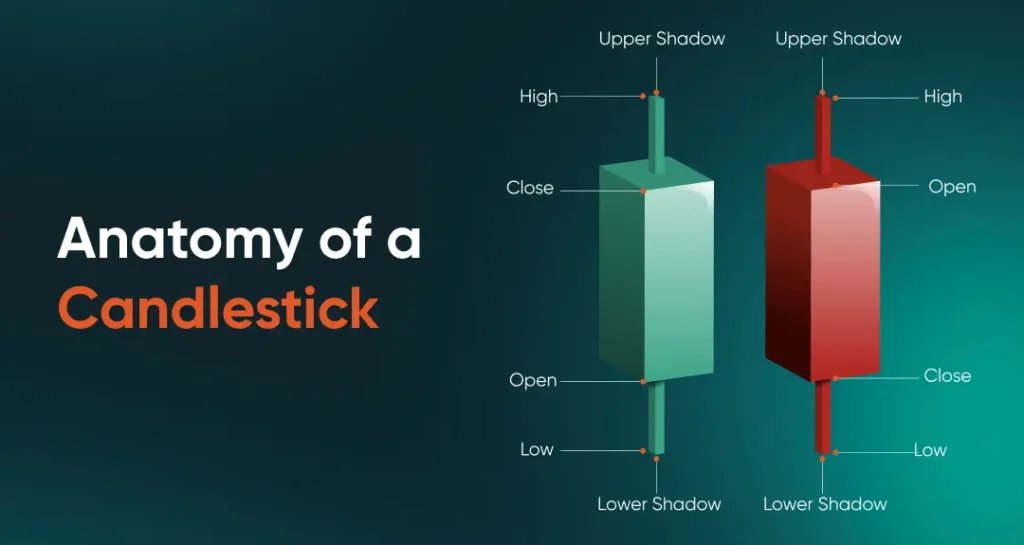
Image 2: Candlestick anatomy
Beyond basic price representation, candlestick charts allow traders to recognise recurring patterns, such as doji, engulfing, and hammer formations. These forex trading chart patterns can help interpret shifts in momentum, potential reversals, or continuation signals within the market.
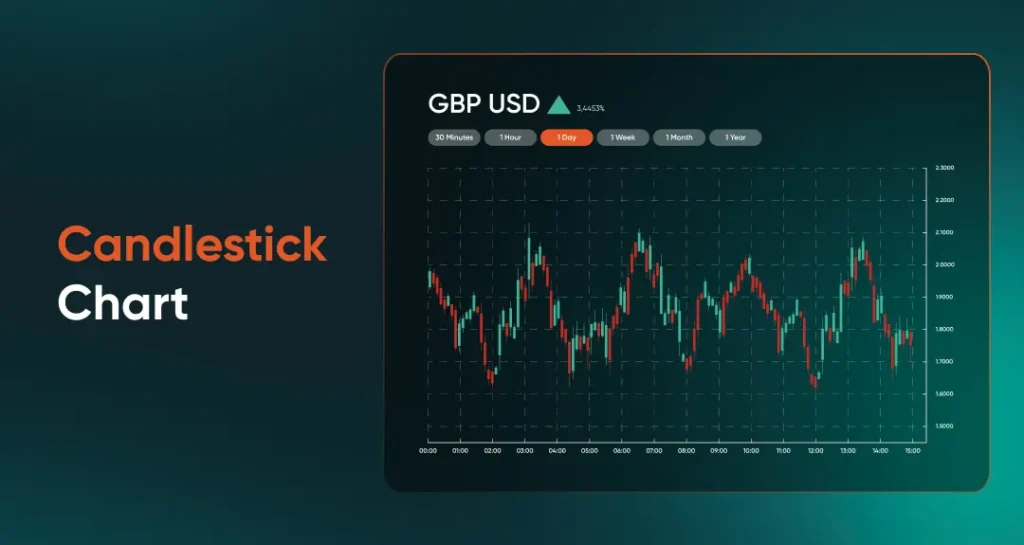
Chart 4: GBP/USD candlestick chart example.
By learning how to read different chart types, traders can better interpret market movements and price trends. To deepen your knowledge, explore our guide on why you should trade forex and gain a clearer view of how the market works.
Understanding Timeframes in Currency Trading Charts
Timeframes define how price data is grouped and displayed on a trading chart. In forex, this could range from one-minute intervals to monthly periods, with each timeframe offering a different perspective on market movement.
Short timeframes, such as one-minute or five-minute charts, highlight rapid price changes and are often used to study short-term volatility. Longer timeframes, such as daily or weekly charts, filter out minor fluctuations, making it easier to identify broader trends in a currency market chart or forex market chart.
Many traders combine multiple timeframes to gain a more comprehensive market view — for instance, confirming a short-term pattern against a longer-term trend. This multi-timeframe approach can provide additional context for interpreting price action.
Forex Chart Analysis Tools
Chart analysis tools help traders interpret data more effectively by highlighting price levels, smoothing out trends, and measuring market momentum. While there are many technical indicators available, three of the most common in forex analysis are support and resistance lines, moving averages, and the Relative Strength Index (RSI).
Support and Resistance Lines in Forex Chart Trading
Support and resistance levels are horizontal lines drawn on a chart to highlight areas where price has repeatedly reversed or paused. Support marks a level where buying interest has been strong enough to prevent further declines, while resistance indicates a price point where selling pressure has consistently capped upward movement.
In the example chart below, you can see multiple minor support and minor resistance levels, along with a strong support zone that price has tested several times. Observing how price reacts to these levels can help identify potential areas where momentum might shift.
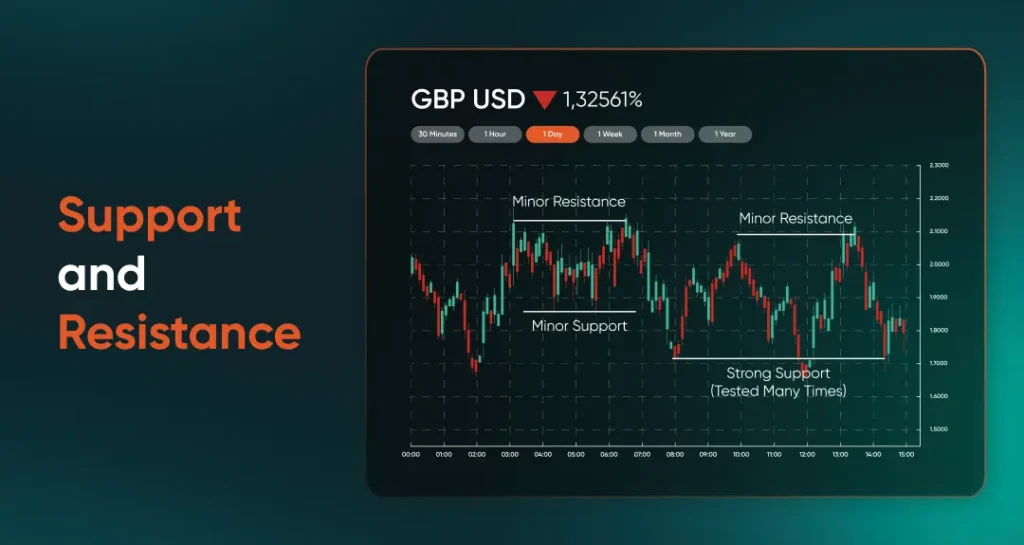
Chart 5: Support and resistance chart example
Notice how the strong support line at the bottom held price from falling further on several occasions.
Moving Averages for Forex Chart Analysis
A moving average smooths out price fluctuations by calculating the average closing price over a set number of periods. This helps traders see the underlying trend more clearly without the “noise” of intraday volatility.
The chart below shows a 50-day simple moving average plotted on GBP/USD. When the price is above the moving average, it often indicates a general uptrend; when it’s below, it may suggest a downtrend.
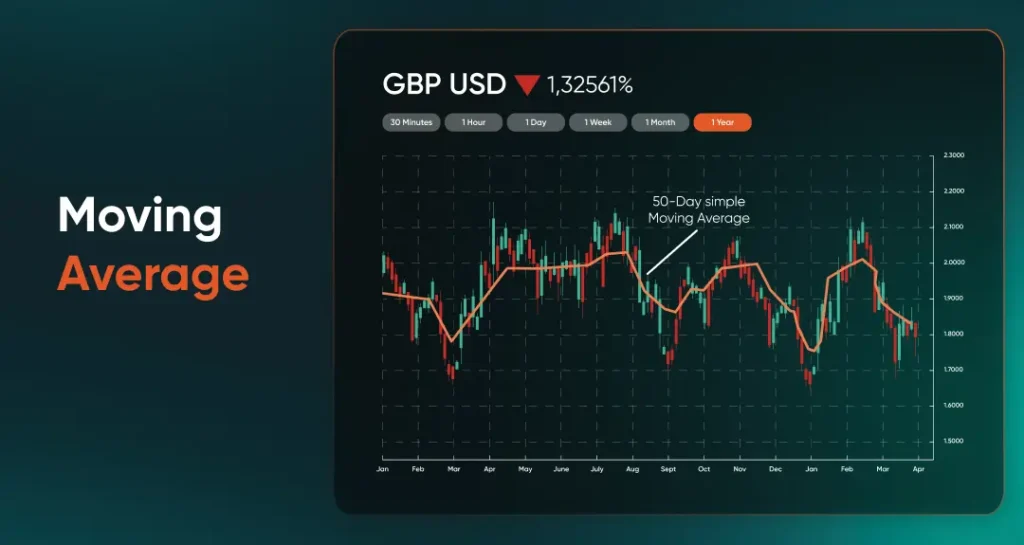
Observe how the moving average line follows the price direction, providing a visual guide to the overall trend.
RSI in Forex Charts (Momentum Indicators)
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) measures the speed and change of price movements, oscillating between 0 and 100. Values above 70 may suggest overbought conditions, while values below 30 may indicate oversold conditions.
By adding RSI to a forex chart, traders can gauge whether recent price moves are strong enough to suggest continuation or if they might be losing momentum.
Vantage’s live forex charts allow you to practise marking these levels in real time, whether you’re tracking EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, or other major pairs. You can also explore past reactions to support and resistance using forex live charts tools.
Enhance your analysis skills by exploring our full guide on forex trading strategies.
Common Forex Chart Patterns and Their Interpretation
Chart patterns are recurring formations on trading charts that can give insights into potential market sentiment and momentum. They are not predictive guarantees but can provide context for interpreting price behaviour.
The image below highlights some of the most popular patterns seen in forex trading:
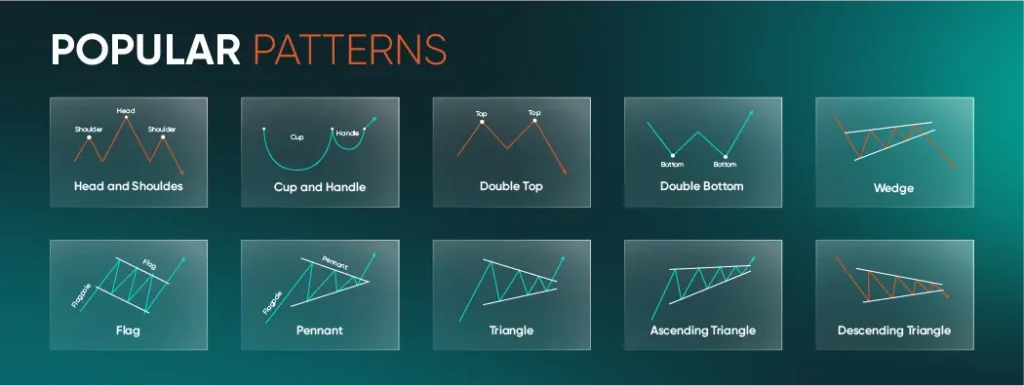
Image 3: Popular trading chart patterns
- Head and Shoulders: Often signals a potential trend reversal from bullish to bearish.
- Cup and Handle: Typically associated with a continuation of an uptrend after a brief consolidation.
- Double Top / Double Bottom: Formations that may indicate a reversal at significant price levels.
- Wedge: Can be either bullish or bearish depending on its slope and breakout direction.
- Flag and Pennant: Short-term continuation patterns following a sharp price move.
- Triangles (Symmetrical, Ascending, Descending): Consolidation phases that can break in either direction, with the slope sometimes suggesting the likely outcome.
When analysing these patterns on a forex chart trading setup, many traders combine them with tools such as moving averages, support and resistance lines, or RSI to confirm market context.
Notice how each pattern has distinct peaks, troughs, or consolidation shapes, which help distinguish one formation from another.
Final Thoughts on Reading Forex Trading Charts
Trading charts are a cornerstone of market analysis, offering a visual way to track price movements and spot potential patterns. By understanding chart types, timeframes, and technical tools, traders can better interpret market behaviour.
Whether you’re reviewing live forex charts for real-time updates or studying historical data on free forex charts, consistent practice is key to building confidence in chart reading.
Open a live account with Vantage to apply your chart analysis skills in real market conditions.
FAQs
How do you read forex charts?
Reading a forex chart involves identifying the currency pair, understanding the price axis and time axis, and interpreting patterns or trends. Traders may also use technical indicators, such as moving averages or RSI, to help analyse market behaviour.
How to read currency trading charts?
Currency trading charts show the exchange rate between two currencies over time. Analysing these charts often involves reviewing historical price data, spotting chart patterns, and applying tools like support and resistance levels to understand possible market movements.
How to read forex trading charts for beginners?
Beginners can start with candlestick charts, focusing on how the body and wicks represent price changes, then explore different timeframes to see how market trends evolve.
How to read a forex chart pattern?
Forex chart patterns are shapes or formations that appear when price movements follow certain trends. Common patterns include head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, and triangles. These patterns can suggest potential market direction, though they are not guarantees of future movement.
How to read trading charts in forex market analysis?
Effective forex market analysis with trading charts means reviewing multiple timeframes, observing price action, and factoring in broader market influences like economic news.




